Fast enhancement on hydrophobicity of poplar wood surface using low-pressure dielectric barrier discharges (DBD) plasma
11:20 - 25/03/2019
Natural durability of the culturally and historically important timber: Erythrophleum fordii wood against white-rot fungi
Shrinkage and swelling behavior of archaeological waterlogged wood preserved with slightly crosslinked sodium polyacrylate
Natural durability of Erythrophleum fordii Oliver against white rot fungi
Shrinkage and swelling behavior of archaeological waterlogged wood treated with polyacrylic acid resin
Applied Surface Science, 407, 412-417, 2017
Authors
- Weimin Chen - Nanjing Forestry University; Jiangsu Engineering Research Center of Fast-growing Trees and Agri-fiber Materials, Nanjing 210037, China; Nanjing Suman Plasma Technology Co., Ltd, Enterprise of Graduate Research Station of Jiangsu Province, No. 3 Youyihe Road, Nanjing 210001, China
- Xiaoyan Zhou - Nanjing Forestry University; Jiangsu Engineering Research Center of Fast-growing Trees and Agri-fiber Materials, Nanjing 210037, China
- Xiaotao Zhang - Nanjing Forestry University; Jiangsu Engineering Research Center of Fast-growing Trees and Agri-fiber Materials, Nanjing 210037, China
- Jie Bian - Nanjing Suman Plasma Technology Co., Ltd, Enterprise of Graduate Research Station of Jiangsu Province, No. 3 Youyihe Road, Nanjing 210001, China
- Shukai Shi - Nanjing Forestry University; Jiangsu Engineering Research Center of Fast-growing Trees and Agri-fiber Materials, Nanjing 210037, China
- Thiphuong Nguyen - Nanjing Forestry University; Jiangsu Engineering Research Center of Fast-growing Trees and Agri-fiber Materials, Nanjing 210037, China
- Minzhi Chen - Nanjing Forestry University; Jiangsu Engineering Research Center of Fast-growing Trees and Agri-fiber Materials, Nanjing 210037, China
- Jinglin Wan - Nanjing Suman Plasma Technology Co., Ltd, Enterprise of Graduate Research Station of Jiangsu Province, No. 3 Youyihe Road, Nanjing 210001, China
Abstract
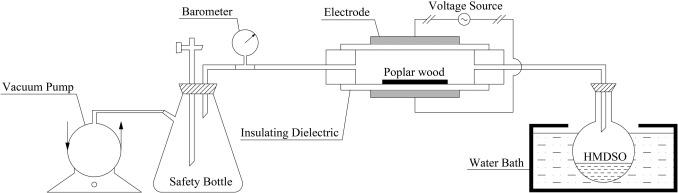
The hydrophilicity of woody products leads to deformation and cracks, which greatly limits its applications. Low-pressure dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma using hexamethyldisiloxane was applied in poplar wood surface to enhance the hydrophobicity. The chemical properties, micro-morphology, and contact angles of poplar wood surface before and after plasma treatment were investigated by attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscope and energy dispersive analysis of X-ray (SEM-EDX), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and optical contact angle measurement (OCA). Moreover, tinfoil film was used as the base to reveal the enhancement mechanism. The results showed that hexamethyldisiloxane monomer is first broken into several fragments with active sites and hydrophobic chemical groups. Meanwhile, plasma treatment results in the formation of free radicals and active sites in the poplar wood surface. Then, the fragments are reacted with free radicals and incorporated into the active sites to form a network structure based on the linkages of Si-O-Si and SiOC. Plasma treatment also leads to the formation of acicular nano-structure in poplar wood surface. These facts synergistically enhance the hydrophobicity of poplar wood surface, demonstrating the dramatically increase in the equilibrium contact angle by 330%.


